
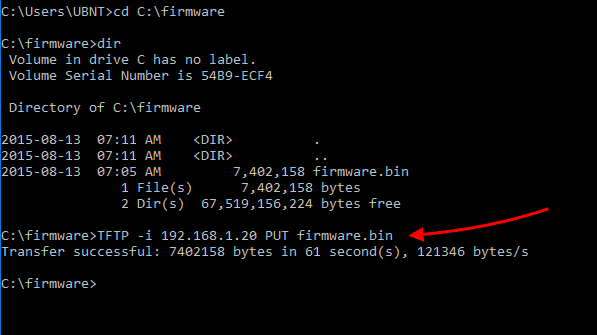
Then device with the broken firmware then has to be started up in TFTP recovery mode. There are two potential modes of operation:įor many routers, the recovery process requires you to host the firmware image on a TFTP server on your computer. In case of a failed flash process or in case of a misconfiguration, the device's boot loader usually remains untouched and can therefore be used to reflash the firmware and recover the device. On most devices, the vendor provides a boot loader on a discreet partition that is untouched by firmware updates.
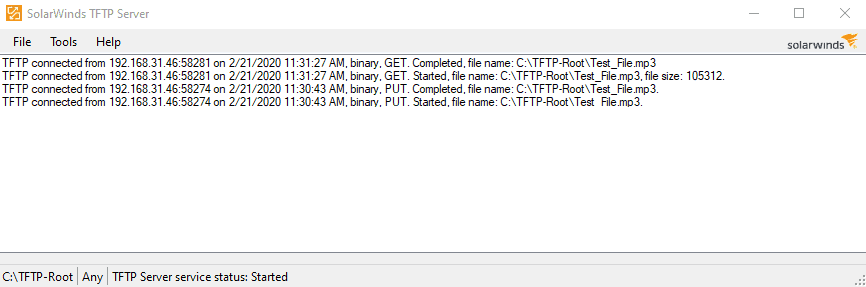
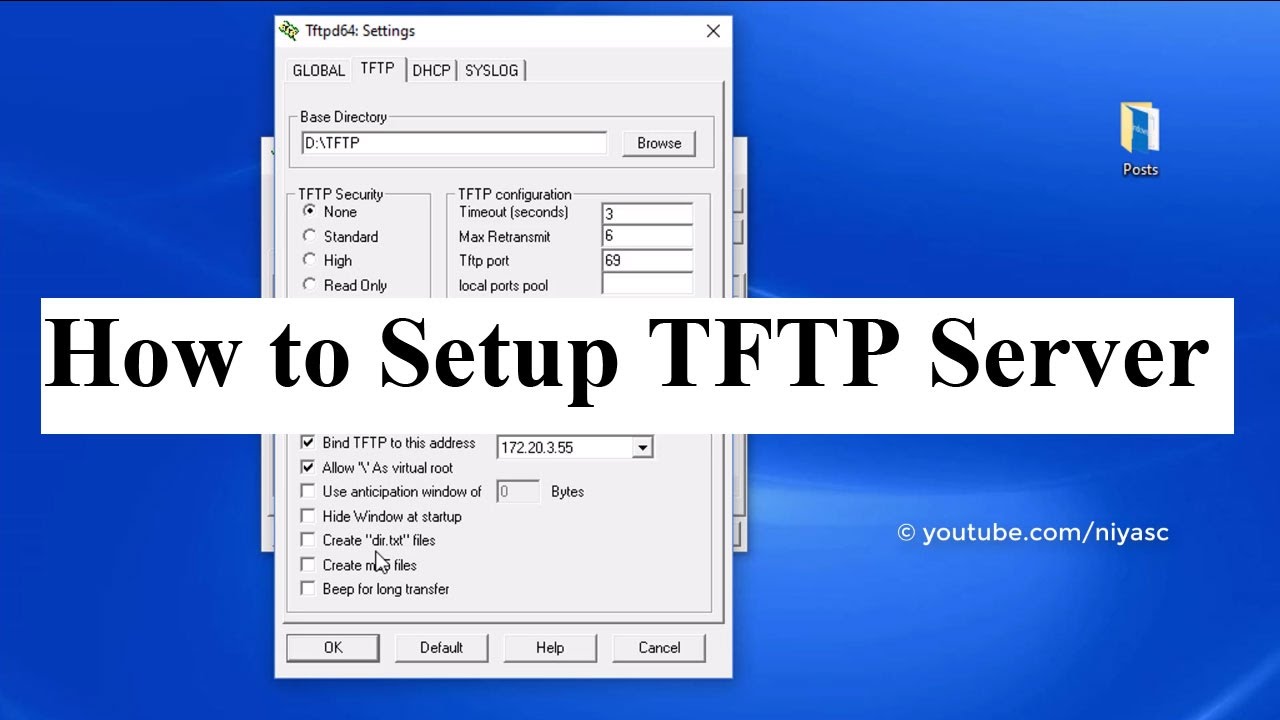
If you keep TFTP-Server running or if you keep the TFTP-client tool available to run anytime, then abusive hackers can abuse/exploit it, to load harmful firmware and/or to change sensitive security settings inside your existing router firmware 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, etc. (frwl rule # 3) TFTP traffic is Not-Allowed when originated from Internet-ip-address (aka: NON private- LAN ip-address ranges)Īnd you must also make sure to do this: after your develop / troubleshooting etc work is done or when you pause to goto other work, then make sure the TFTP-server and TFTP-client both are completely disabled in your OS/distro : turn off TFTP-Server service / process, disable TFTP-server startup script file, and move the TFTP-client ( tftp) & the TFTP-server ( tftpd) executable / binary ( bin) files out of all folders mentioned in your PATH variable, into a different folder (which is NOT in the PATH variable), and also move bin files out of the folder which is mentioned in startup-script (if such is used).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
